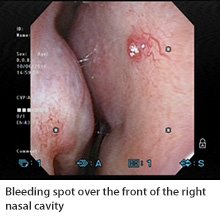
The medical term for nose bleeds is epistaxis – a common condition that affects all age groups and sexes. However, the cause and intensity of these nose bleeds may differ.
Causes
-
Local Trauma
-
Clotting Disorders / Hereditary Blood Vessel Disorders
- Patients with clotting disorders may experience nose bleeds with the slightest nasal trauma
- Hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia (causes dilated blood vessels in the nose) can sometimes cause torrential epistaxis
-
Benign Nasal Tumours
- Inverted papillomas: Fleshy looking benign nasal tumours that cause nose bleeds
- Usually not torrential – just blood stained nasal secretions
- Juvenile Angiofibroma: A rare benign tumour that can cause torrential nose bleeds in children and teenagers
-
Malignant Nasal Tumours
- Most common malignant tumour in this region is nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC)
- Blood stains in the phlegm, enlarged lymph nodes, blocked ears and diplopia
- Less common: sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma, nasal lymphomas
If a tumour is detected or suspected, a biopsy will be required to confirm the diagnosis. Further scans like the CT/MRI scan may be required as well to determine the extent of the tumour.
Treatment
Most of the time, nose bleeds are mild and will stop on their own within a few minutes.
Tips to Stop a Nose Bleed:
- Pinch the soft part of your nose
- Lean forward slightly
- Place a cold towel or a pack of ice over the bridge of your nose
- Suck on an ice cube
However, if the bleeding is severe and persists beyond 20-30 minutes, you will need to see an ENT doctor immediately. If it occurs after office hours, you may need to visit the Emergency department.
Most severe cases of nose bleeds stop after 48-72 hours of packing. Those that do not stop even then may require surgery or embolization.